Learning How to Die in the Anthropocene
I.
“…a civilization in collapse, with a crippled infrastructure, unable to recuperate from shocks to its system.”
It’s impossible to argue that the future is going to be more unreliable and extreme than the past, but equating it to the shock and awe of the US Armed Forces in Iraq also seems excessive. It’s hard to argue against the author’s experiences, since he was on the ground in Baghdad and New Orleans, but it’s also hard for me to accept that the instability he witnessed in Baghdad and New Orleans will become the new normal. We are going through a series of rough lessons now, but it’s hard for me to imagine that we will not learn from them. The timescale of the invasion of Iraq and the creep of the Anthropocene are two totally different things.
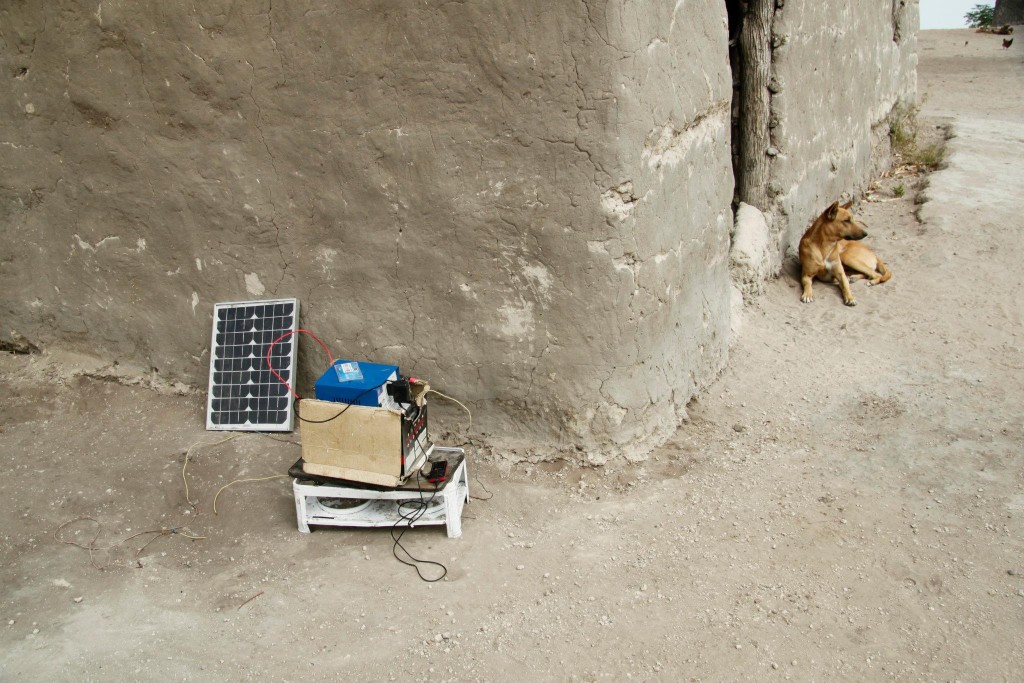
I’m just responding to personal experiences with more personal experiences, but living through Hurricane Irene, Superstorm Sandy, and the recent Snowstorm Jonas I feel like I’m watching the shift in expectation and policy that life in the Anthropocene necessitates. The public reaction to Irene and Sandy seem especially revealing. The ‘no show’ of Irene was met with frustration and incredulity about future threats to the city, but Sandy wiped that smile off of everyone’s face. I think that, in New York at least, people are more willing to accept that there are going to be extreme events and that how we think of them needs to change, both in policy and in individual behavior. Now is the time to think about how institutional policy must be changed to make it more flexible and how citizen responsibility will need to fill in the gaps. We are going to need local and national governments that are prepared for the unknowable. We are also going to need to think about how individuals and households can be prepared. The future is going to have much so more anxiety and uncertainty than the past, but it’s not like we can’t live through it.
Questions:
In what ways is it possible to introduce both government flexibility and citizen self reliance into how we think about society and government?
How do we put pressure on institutions to do better, while equipping ourselves to deal on a personal, human level? (Look at digging out Queens from the recent snowstorm for example. Could the city have had a better plan with existing resources, or do we need more snowploughs?)
Are there simple, multipurpose tools that can be introduced to help? Something that is the equivalent of a good sharp shovel, a workhorse with elegant design that can be used for many different things.
What does the aftermath of a hurricane look like now in somewhere like Florida, where they are normal? How does citizen preparedness meet government efforts?
Relevant Links:
http://occupysandy.net/
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/10/27/magazine/could-new-york-city-subways-survive-another-hurricane.html?pagewanted=all
II.
“The biggest problem we face is a philosophical one: understanding that this civilization is already dead.”
This is the part of the article that I found much more compelling. The planet is dying, how do we mourn and memorialize the world that was as it passes in front of our eyes? Who is the audience for such memorials? People now, or people in the far away future? How do you commemorate the passing of a civilization? What is the precedent for something like this? How does everyone feel?
The Challenge of Responsible Design
“The science we have, and the technology we have both are always and inevitably a function not simply of ‘reality,’ but of where our attention happens to be focused.”
This is particularly striking to me. It’s something that I know is true, but it’s good to be reminded of it. I tend to be a practical thinker, interested in what is feasible in problem solving. I often find myself limiting my options to the possible, politic decision and find myself detracting from more far out ideas as being “unreasonable”. I think this is something that starkly limits my imagination of the future, not just in design projects but generally in my day to day life.
Design + Research
A lot of good points, but this is written as insufferable academic nonsense. Why write something this way? Why not just write something in a way that people can read it? Was this translated into English from another language, or what?
It is good to have criticism in design, but I think it’s easy to go down a rabbit hole. Spending too much time on criticism can be paralyzing to action, which so much design is based around. This might not even be relevant to my practise in this class. As the authors note: “Indeed, it might be difficult for interaction design – and perhaps even for design research – to rest on any singular or stable set of foundations.” The main focus of ‘practical’ criticism seems to be to make sure that your project is fit for its purpose as you’ve defined it, and to keep revisiting the definition. Being nimble in design practise seems more relevant than anything else.
Designing Interactions
Is interaction design actually meta design?
There are a number of interesting designs from Dunne and Raby, but it’s interesting that a lot of the books and writings that they cite as inspiration are already popsci books. It’s like they’re deriving a derivative, instead of reading research directly. I mean, it’s not like they don’t go back to hard research, but I can’t help but feel like their work is a little like ‘toy’ work. I see the value of rethinking these ideas, and even doing it in an ‘unreal’ way that pushes outside of our normal thinking, but I feel like I don’t know who the audience for this work is. Other designers? Scientists? How much do ‘normal people’ encounter work like this? They mentioned recruiting people for the placebo work through ads and other everyday means, but where does the work go after that? Into a design book somewhere? (Aside, where does any work go ‘after’?)